This briefing analyses the global and European nickel market and explores some of the challenges and solutions to the issues associated with nickel mining and processing, such as emissions, waste management and biodiversity issues.
Main findings
- Nickel will continue to be a critical material for electric vehicles batteries, with nickel-containing chemistries making up for around half of the global market in 2030.
- The nickel supply expansion will continue to come from Indonesia, accounting for 60% of the global nickel mined output and 40% of the refined output by 2030.
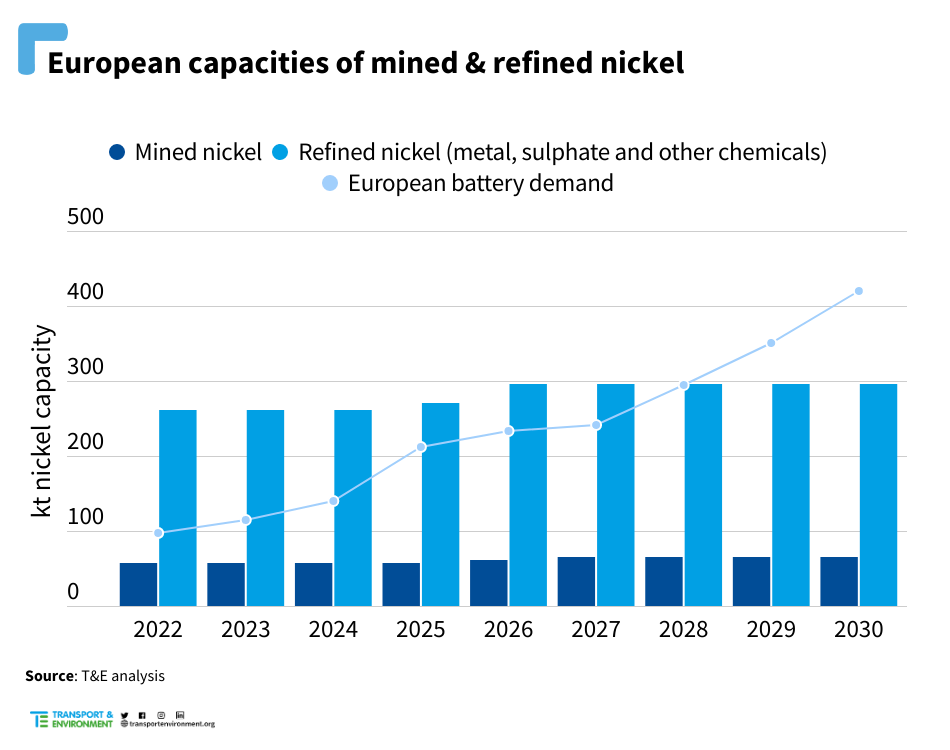
- In Europe, mining capacities can meet up to 16% of the future demand from batteries. Refining capacities could cover between 15% and, theoretically, 70%, should volumes allocated for other applications be diverted to batteries and planned expansions materialise.
- Nickel sulphate production operations with access to renewable energy and using hydrometallurgical technologies, such as bioheap leaching and pressure oxidation, have emissions that are 63% and 70% respectively lower than the industry average. The NPI to matte production route, commonly used in Indonesia, generates 5 times more emissions than the industry average.
- Switching to renewable sources of electricity alone can reduce emissions by up to 40% on average.
- Adopting best available practices and technologies for waste management (e.g. dry stacking) and biodiversity conservation (e.g. habitat restoration programs from dedicated budgets) will be key for ensuring responsible mining.
- Robust industrial and environmental policies are needed to ensure nickel’s production becomes cleaner, including expanding nickel processing capacities in Europe, setting up mutually beneficial trade partnerships with nickel-rich countries and investing in renewables infrastructure.
The fast evolving nickel market
The green transition will require a substantial supply of raw materials, with nickel emerging as a critical enabler of this transformation. In this paper T&E looks at the current nickel market globally, Europe’s potential, and the ways to source nickel sustainably.
Nickel in lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles provides longer driving ranges and battery chemistries are evolving rapidly. The currently popular high-nickel chemistry (NMC 811) contains around 0.66 kg Ni/kWh, but alternative chemistries with lower content are emerging. In 2030, nickel-containing chemistries are expected to account for around half of the global market.
To keep up with the rising demand driven by the widespread adoption of electric vehicles, nickel production will need to expand. A significant portion of the global nickel supply – around 60% of the mined output and 40% of the refined output by 2030 – will originate from Indonesia, which has rapidly grown into a nickel powerhouse in recent years.
Nickel demand and production capacities in Europe
In Europe, the nickel mining capacities potentially relevant for the battery sector could reach 66 kt Ni, meeting 16% of the region’s demand from electric vehicles and energy storage systems in 2030. Refining capacities of nickel sulphate – the material of choice for these batteries – amount to 63 kt Ni, or 15% of the region’s future battery demand, with a potential expansion, albeit uncertain, of 35 kt (8%). Demand coverage would be even higher if some of the metal capacities were diverted to this sector, meeting up to around 70% of the demand. However, this would not account for other competing applications and remains uncertain.
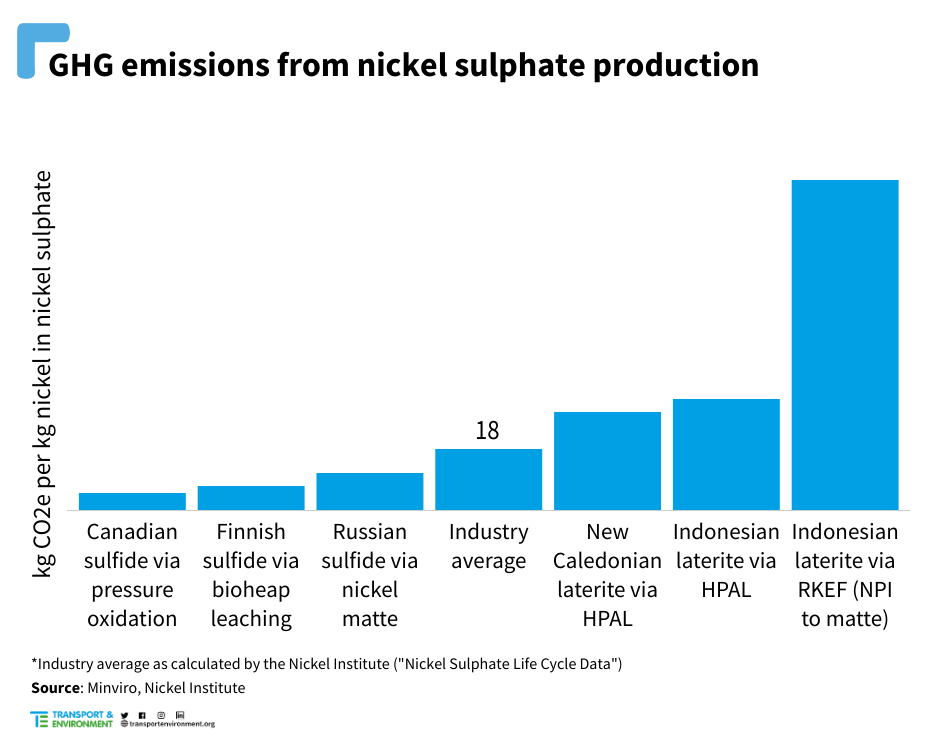
Reducing GHG emissions is key to improving nickel’s environmental credentials
Nickel mining and refining comes with a certain carbon footprint, but there are solutions to improve this environmental impact. Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions vary widely across nickel sulphate production sites, depending on multiple factors including the energy source and production technologies deployed. Analysis by Minviro shows that operations with access to renewable energy and using hydrometallurgical technologies, such as bioheap leaching and pressure oxidation, have the lowest carbon footprint. Specifically, a comparison of six nickel sulphate production routes reveals that emissions levels at the best performing facilities, located in Canada and Finland, are 70% and 63% lower, respectively, than the industry average. At the opposite end, processing laterite ores into nickel pig iron (NPI) to matte to nickel sulphate generates 5 times more emissions than the industry average, while the high pressure acid leaching (HPAL) route, increasingly popular in Indonesia, produces almost twice as much emissions than the industry average.
GHG emissions vary widely across nickel production sites, depending on ore, location, technology and energy source
Studies show that switching to renewable sources of electricity alone can reduce emissions by up to 40% on average. Other key solutions to mitigate the industry’s GHG emissions include using zero-carbon chemicals in the processes, decarbonising mining vehicles, streamline logistics and developing and adopting more efficient ore processing techniques that require less energy, such as bioheap leaching and pressure oxidation for sulphides, as well as heap leaching and atmospheric hydrometallurgical processing for laterites.
Policies can enable cleaner nickel production
However, policies are needed to ensure nickel’s production becomes cleaner. These include increasing renewables share in the energy mix, defining cleaner low emission nickel refining and processing routes (e.g. via EU Taxonomy Regulation) to stimulate investments in hydrometallurgy-based technologies, and mandating the use of best available technologies (e.g. for waste management and biodiversity conservation). Globally, applying robust standards such as the Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance (IRMA) to more mining sites will improve environmental and social stewardship.
In Europe the focus should be on creating a local battery value chain as part of the EU Critical Raw Materials Act, with support for strategic projects that adhere to strict environmental and social standards, and forward looking industrial strategy centred around targeted funding support (e.g. via the EU Innovation Fund). In addition, collaborating with nickel-rich countries, investing in sustainable large-scale projects abroad and sharing expertise will be key for establishing mutually beneficial trade relationships.
Key recommendations
- Domestic processing capacities: Expand sustainable nickel processing capacities through investment incentives (e.g. via the EU Innovation Fund), infrastructure development and the attraction of a skilled workforce. Promote Strategic Projects in nickel processing, ensuring these benefit from streamlined permitting and financial support, while adhering to strictest environmental and social standards and with local communities on board.
- Trade partnerships: Collaborate with nickel-rich countries via trade partnerships and create a framework for the public and private investments into nickel projects abroad, provided high environmental and social criteria are guaranteed.
- GHG emissions: Prioritise grid decarbonisation by investing in renewables infrastructure; develop and enforce regulations that set emission reduction targets for the extractive sector; and mandate the use of renewable energy sources in mining, refining and all manner of extractive operations.
- Waste management: Require the implementation of best tailings management practices, such as designing facilities to withstand location-specific severe weather-related events as well as mandate the use of best available technologies, such as dry stacking of filtered tailings.
- Biodiversity conservation: Require companies to implement habitat restoration and reforestation programs in areas affected by mining activities throughout the life cycle of the mines, along with the establishment of well-funded compensation budgets for these rehabilitation activities.


