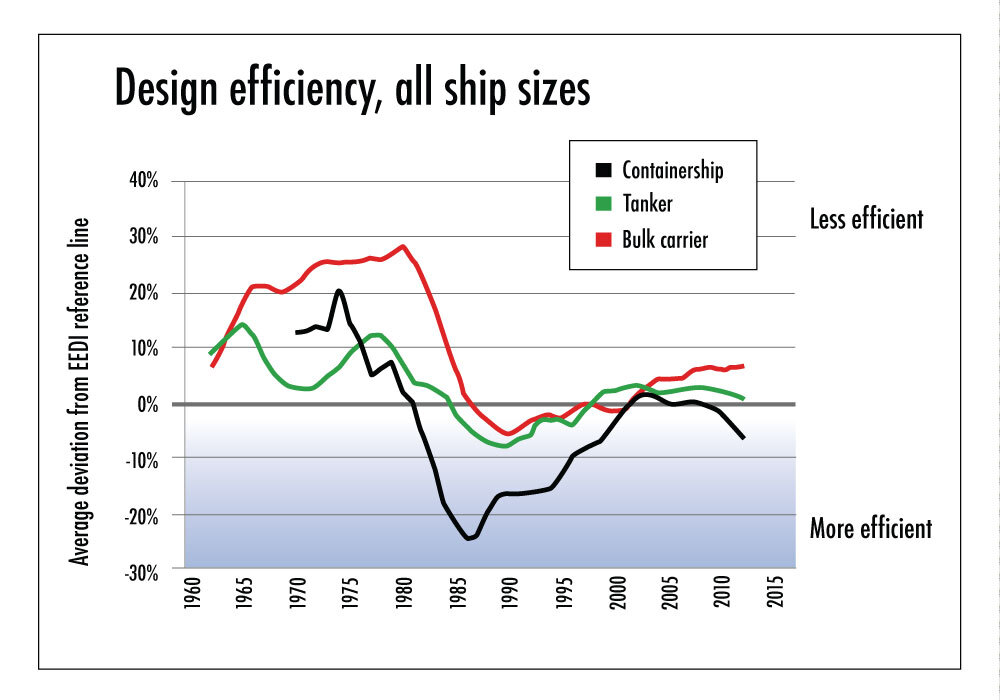
This first ever study of the historical development of the design efficiency of new ships, commissioned by Seas At Risk and Transport & Environment, finds that bulk carriers, tankers, and container ships built in 2013 were on average 12, 8 and 8% less fuel efficient than those built in 1990, a quarter of a century ago.
The findings contradict claims that shipping has been constantly improving its environmental performance. They also demonstrate that market forces by themselves don’t result in more fuel efficient ships being built. Oil prices in the late 1980s and early 1990s, the time when new ships were historically most fuel efficient, were around a quarter of the levels seen in the 2008-2013 period (ca $25 vs $100 per barrel, in today’s prices).
John Maggs, policy advisor at Seas At Risk and president of the Clean Shipping Coalition, said: “Now we know that we cannot rely on rising fuel prices, other market forces or the good intentions of industry to solve shipping’s climate problem. Instead we need a clear and ambitious target for reducing ship greenhouse gas emissions and legally binding measures to get us there.”
The IMO will review the stringency levels of its Energy Efficiency Design Index (EEDI) – the efficiency standards for new ships – during a meeting of its Marine Environmental Protection Committee (MEPC) in London next month.
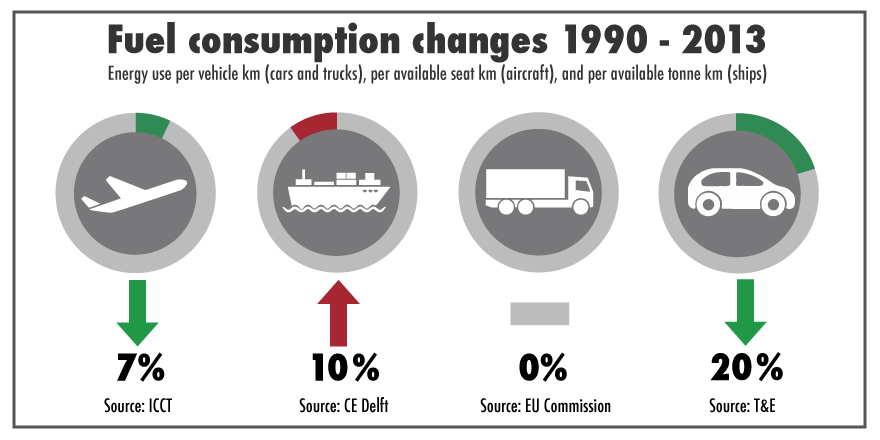
Bill Hemmings, clean shipping manager at Transport & Environment, said: “The truth is out! Aircraft and cars have become more fuel efficient, but despite a generation of technological improvements, ships have largely gone backwards for most of the past 25 years. The IMO’s design efficiency standard for new ships itself needs a redesign and strengthening if the standard is not supposed to merely bring us back to levels achieved 25 years ago.”